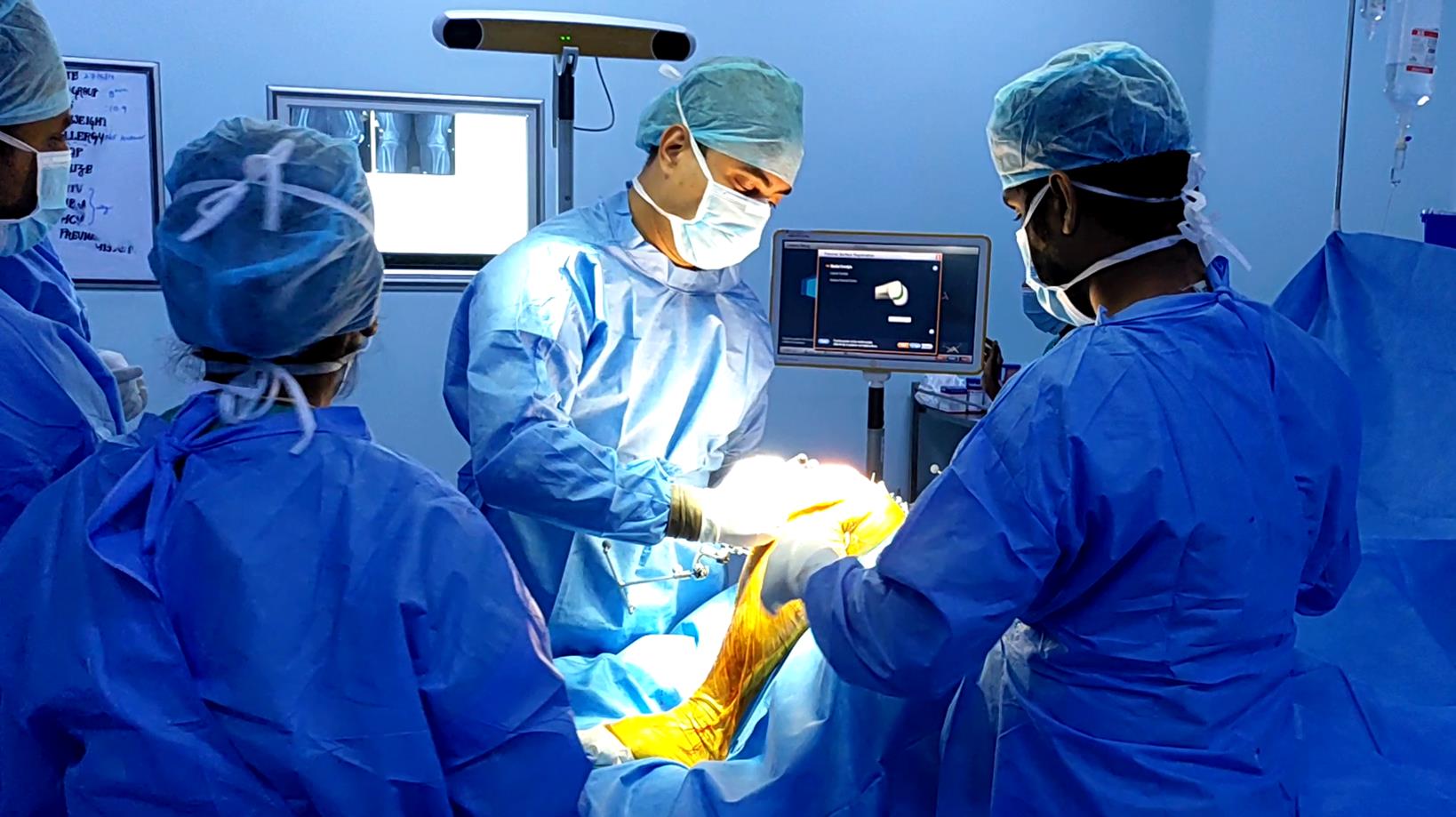
what is a knee cap (patella)?
The knee cap is a floating bone, which sits on the front of the knee joint and it helps in the bending and straightening motions of the knee. If the knee cap does not move properly, this is known as a tracking issue. Patella tracking issues and misalignment may cause pain in the knee cap.
What is a knee cap subluxation or dislocation?
Your kneecap is held in place by ligaments and tendons. The kneecap can slide to the side of the knee joint if it is hit with a strong force. This sliding is called subluxation or dislocation. In a dislocation, the kneecap moves farther away from its normal position.
Tags
What are the Causes for knee cap dislocation?
The kneecap may become unstable and thus becomes liable to dislocation owing to the following factors.
- Abrupt swinging or rotation of the body with a solidly planted foot
- Direct impact on the patella with a solid object
- In children, it may also occur when there is anatomical abnormality of the knee joint or there is alignment issues in the lower limb.


What are the symptoms of knee cap dislocation?
Symptoms of knee cap dislocation includes
- Pain when standing up from a sitting position
- Feeling that the knee may buckle or give way.
- Severe pain, swelling, bruising, visible deformity and loss of function of the knee.
- Sensational changes such as numbness or even partial paralysis may be present because of pressure on nerves and blood vessels.
Diagnosis
Various tests are used clinically in an attempt to diagnose patellar instability
X-rays are often used to confirm a dislocated patella. If the individual presents with a history of first-time patellar dislocation that has already been relocated, X-rays may not be helpful.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can be used to identify bone bruising patterns consistent with recent patellar dislocation, cartilage injury and medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) integrity.
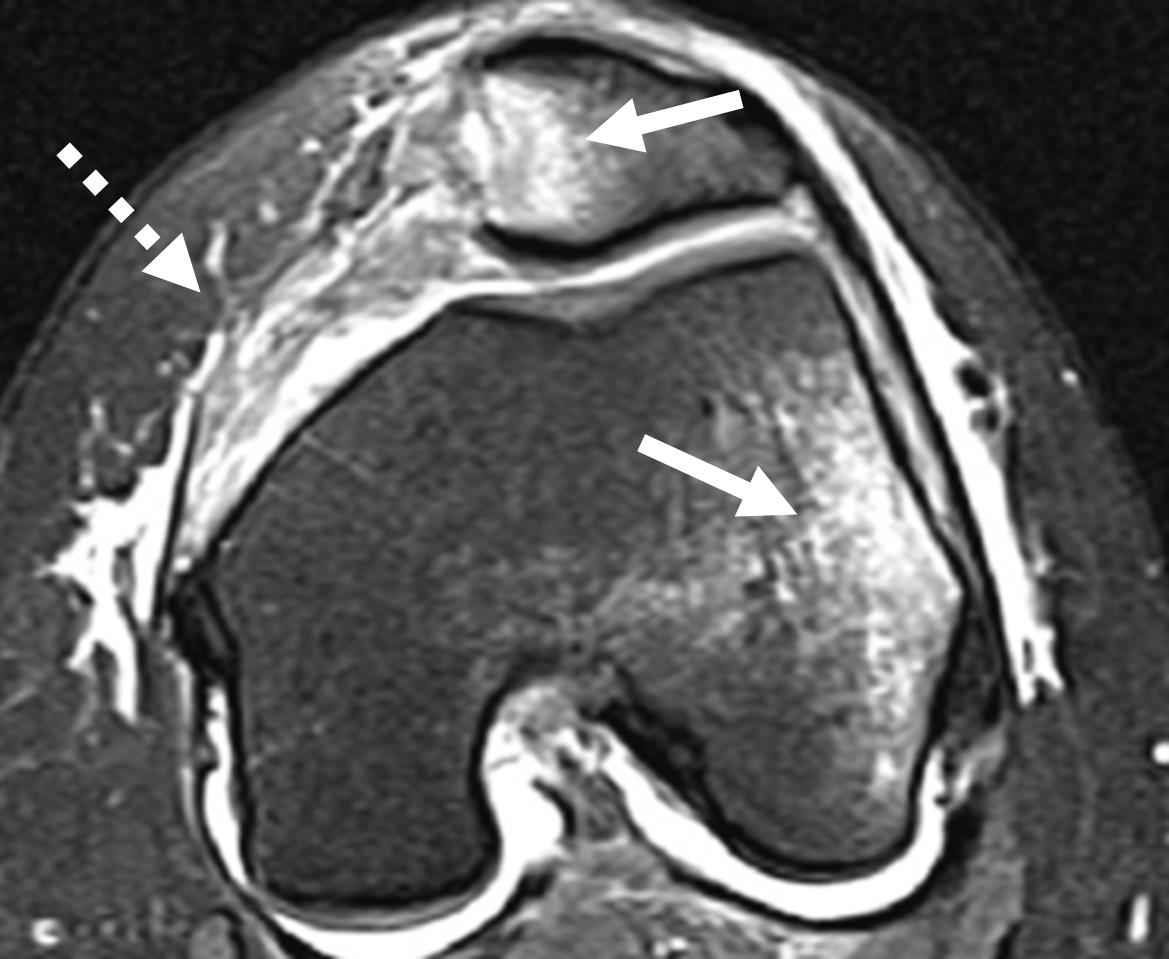
What are the treatment options for patella dislocation?
Once the diagnosis is clear, the dislocation is reduced. Knee immobilization will keep the patella in position until the ligaments heal, usually for about 3 weeks. During this time, weight bearing is not advised.
Physical therapy is important after the cast is removed, to build up muscle strength and range of motion at the joint. The patient is typically able to resume normal activity in about 3-6 weeks, depending on age, health, and severity of the injury.
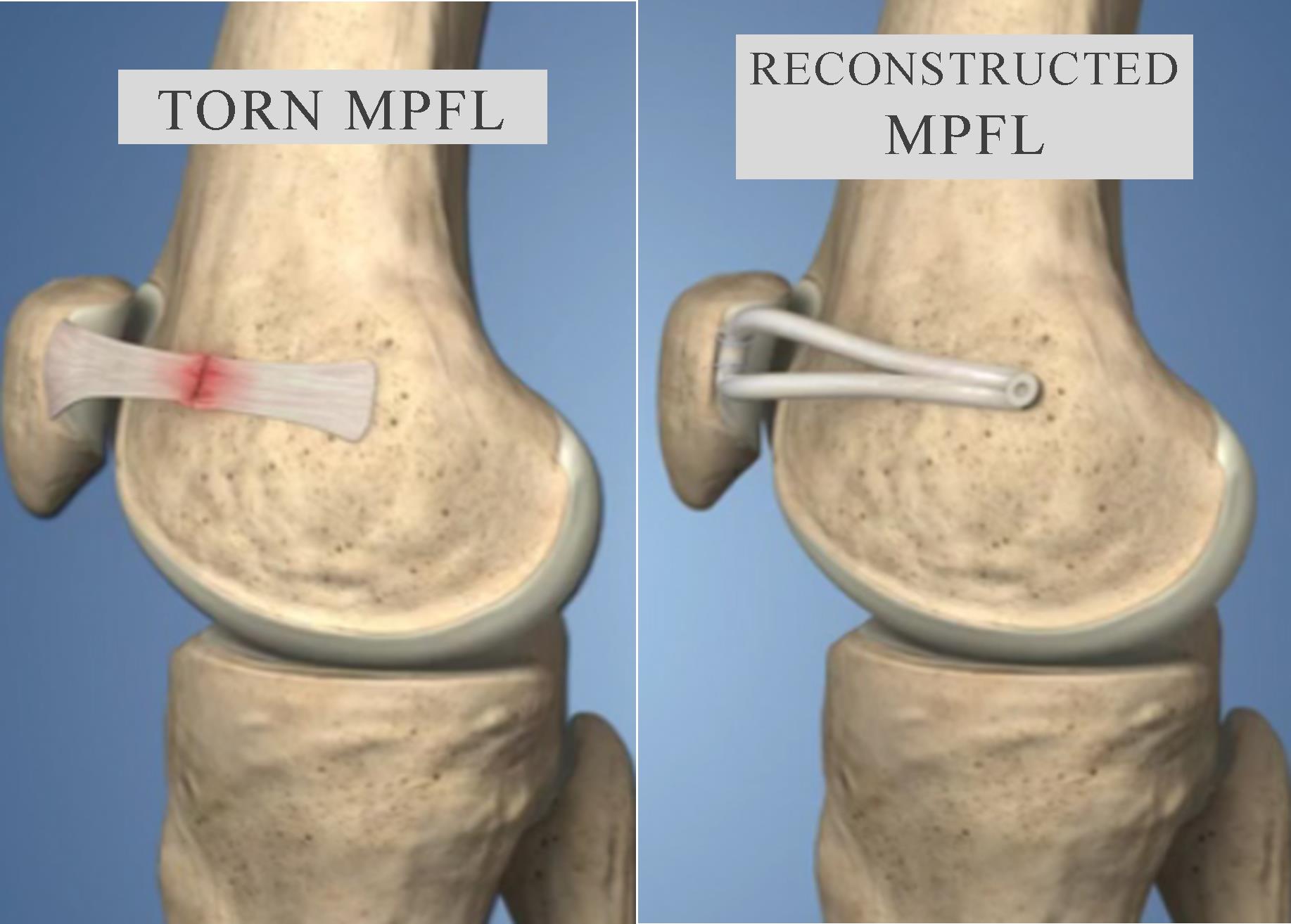
Arthroscopic or sometimes open repair may be done if the bone or cartilage is damaged or there is persistent instability at the kneecap. Congenital abnormalities of the bones should also be corrected to prevent recurrences. If the medial patella femoral ligament is torn it is reconstructed with patients own graft tissue (auto graft).
For further more details, contact Dr.Raj Kanna has a best experience in Knee cap dislocation surgery of affordable cost in Chennai.

